Media Center
Leading neuroscientist and AI geneticist Anders Dale, Ph.D. named president of J. Craig Venter Institute and joins Board
Through two multimillion-dollar NIH grants, Dr. Dale will continue leading key centers for the largest long-term studies of brain development and child health in the United States
Researchers design tools to develop vaccines more efficiently for African swine fever virus (ASFV)
The reverse-genetics system developed for ASFV may be adapted for other viruses, including lumpy skin disease, Zika, chikungunya, and Ebola viruses
Statement on cuts to National Institutes of Health funding
Disruptions or reductions in funding may irreparably harm biomedical research efforts at J. Craig Venter Institute and in the broader research ecosystem
Revolutionizing plastic waste management through biological upcycling
Innovative research transforms plastic waste into valuable chemicals, paving the way for a circular economy and sustainable space travel
Researchers call for global discussion about possible risks from “mirror bacteria”
Advocacy in Action: Effective Techniques for Shaping Science Policy
J. Craig Venter Institute awarded 5-year, $5M grant to lead Center for Innovative Recycling and Circular Economy (CIRCLE)
CIRCLE is one of the six new NSF Global Centers focused on advancing bioeconomy research to solve global challenges
Scientists discover molecular predictors of toxic algal blooms that pose health risk, ecological and economic harm
Genes in the algae Pseudo-nitzschia genus have been identified that act as a warning beacon for a dangerous neurotoxin
Prebys Introduces 2024 Grant Funding to Enhance Career Opportunities for Youth Across San Diego County
Organizations Receiving Part of the $5.89 Million Foster a Thriving San Diego Workforce
Prebys funds 24 grantees as part of a commitment to ensuring San Diego County youth are thriving and actively engaged in their communities
Passing of former J. Craig Venter Institute Trustee Bill Walton
Pages
Media Contact
Related
Newly Discovered Human Brain Cell: Rosehip Neurons
What’s next for exploring the newly discovered human brain cell, the rose hip neuron? We caught up with Dr. Richard Scheuermann on the road to discuss how the J. Craig Venter Institute is advancing knowledge about what makes humans unique. See the full press release.
Ocean Sampling Day 2018
J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI) scientists, led by Lisa Ziegler Allen, PhD, are collaborating with Kelly Goodwin, PhD (NOAA), Brian Palenik, PhD (UCSD), and Maitreyi Nagarkar (UCSD) to participate in this year’s Ocean Sampling Day on June 21. The team, which also includes Sarah Schwenck...
J. Craig Venter Institute Education Program Fosters Learning Opportunities with Salisbury University Students and Faculty
Patti Erickson, PhD first connected with the J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI) in the Fall of 2016 as an associate professor at Salisbury University looking for opportunities to expose undergraduate students to biology outside of the classroom. Soon thereafter, she and a group from Salisbury...
JCVI Makes Strides in Microbial Analysis of Artwork which May Lead to Better Preservation
Through the da Vinci DNA Project, researchers at JCVI began taking samples from aging artwork with the aim of understanding which microbial species are present are present on each.
BioVision Alexandria 2018
The BioVision Alexandria conference convened at the Bibliotheca Alexandrina, in Alexandria, Egypt this past April. The Bibliotheca Alexandrina is a commemoration of the Ancient Library of Alexandria and an attempt to rekindle the global cultural and scholarship role of the library....
J. Craig Venter Institute Inspires Kids on “Take Your Child to Work Day”
Last month when my kindergarten-aged daughter brought home a note from school to dress up as their future career choice, I was pleasantly surprised to hear from her that she aspired to be a scientist just like me. So, we dug through my clothes and found her an old lab coat and decorated the...
JCVI to Receive Grant from Chan Zuckerberg Initiative to Define the Language of Human Cell Classification
Researchers at J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI), led by Richard Scheuermann, PhD, director of JCVI’s La Jolla Campus, have been awarded a grant from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative DAF, an advised fund of Silicon Valley Community Foundation as part of the Human Cell Atlas project. JCVI will be...
J. Craig Venter Institute Teaches Students about Genomics at Annual High Tech Fair
In January, JCVI was one of more than 40 San Diego STEM-related organizations who participated in the Fleet Science Center’s annual High Tech Fair. This year more than 3,000 local middle and high-school students, their teachers, and families descended upon Balboa Park throughout the...
Dr. Scheuermann featured on the Illumina Genomics Podcast
In Episode 14 of the Illumina Genomics Podcast, Dr. Richard Scheuermann is the featured guest. Dr. Scheuermann discusses advancements in cell ontology, informatics, machine learning, and how his approach to biology has adapted over the years to incorporate the massive increases of data and...
New Method for Genome-wide Engineering of Viruses
Researchers at JCVI have been developing synthetic genomics assembly methods since 2000, addressing fundamental biological questions. Together, with researchers at Oregon Health and Science University, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Synthetic Genomics, Inc., and Vir Biotechnology,...
Pages
Scientists Unveil a More Diverse Human Genome
The “pangenome,” which collated genetic sequences from 47 people of diverse ethnic backgrounds, could greatly expand the reach of personalized medicine.
First human ‘pangenome’ aims to catalogue genetic diversity
Researchers release draft results from an ongoing effort to capture the entirety of human genetic variation.
Scientists Create the Smallest-Ever Moving Cell
Just two genes get tiny synthetic cells moving, offering clues to life’s evolution.
From Sequencing to Sailing: Three Decades of Adventure with Craig Venter
In a plenary public appearance at the Molecular and Precision Med TRI-CON event in San Diego, a relaxed Venter reflected on his career highlights, controversies and future priorities for genomic medicine.
Synthesizing life on the planet
What’s the smallest number of genes that cells need to grow and reproduce? Is it possible to synthesize minimal genomes and insert them into cells? What do minimal genomes teach us about life? An interview with John Glass, Ph.D.
Top scientists join forces to study leading theory behind long COVID
Several JCVI scientists will be contributing to the newly launched Long Covid Research Initiative — a collaboration of researchers, clinicians, and patients working to rapidly study and treat long Covid.
Hunting for deep-ocean plastics
Through the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, National Deep Submergence Facility, JCVI's Erin Garza, Ph.D. joins a deep sea expedition to search for ocean plastics aboard the HOV Alvin.
A journey to the center of our cells
Biologists are discovering the true nature of cells—and learning to build their own.
Dr. Hend Alqaderi on paving the way for women in science in the GCC
Hend Alqaderi, a JCVI collaborator and mentee to Marcelo Freire receives the L’Oréal-Unesco Women in Science award
Pages
Logos
The JCVI logo is presented in two formats: stacked and inline. Both are acceptable, with no preference towards either. Any use of the J. Craig Venter Institute logo or name must be cleared through the JCVI Marketing and Communications team. Please submit requests to info@jcvi.org.
To download, choose a version below, right-click, and select “save link as” or similar.
Images
Following are images of our facilities, research areas, and staff for use in news media, education, and noncommercial applications, given attribution noted with each image. If you require something that is not provided or would like to use the image in a commercial application please reach out to the JCVI Marketing and Communications team at info@jcvi.org.
Human Genome

The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter
gff2ps achieved another genome landmark to visualize the annotation of the first published human diploid genome, included as Poster S1 of “The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter” (Levy et al., PLoS Biology, 5(10):e254, 2007). Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).

Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly
We have drawn the map of the Human Genome with gff2ps. 22 autosomic, X and Y chromosomes were displayed in a big poster appearing as Figure 1 of “The Sequence of the Human Genome” (Venter et al., Science, 291(5507):1304-1351, 2001). The single chromosome pictures can be accessed from here to visualize the web version of the “Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly” poster. Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).
Synthetic Cell

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D. and Hamilton O. Smith, M.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Hamilton O. Smith, M.D. and Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D.
Credit: Brett Shipe / J. Craig Venter Institute

Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

John Glass, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Dan Gibson, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Carole Lartigue, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Synthetic Biology Team
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
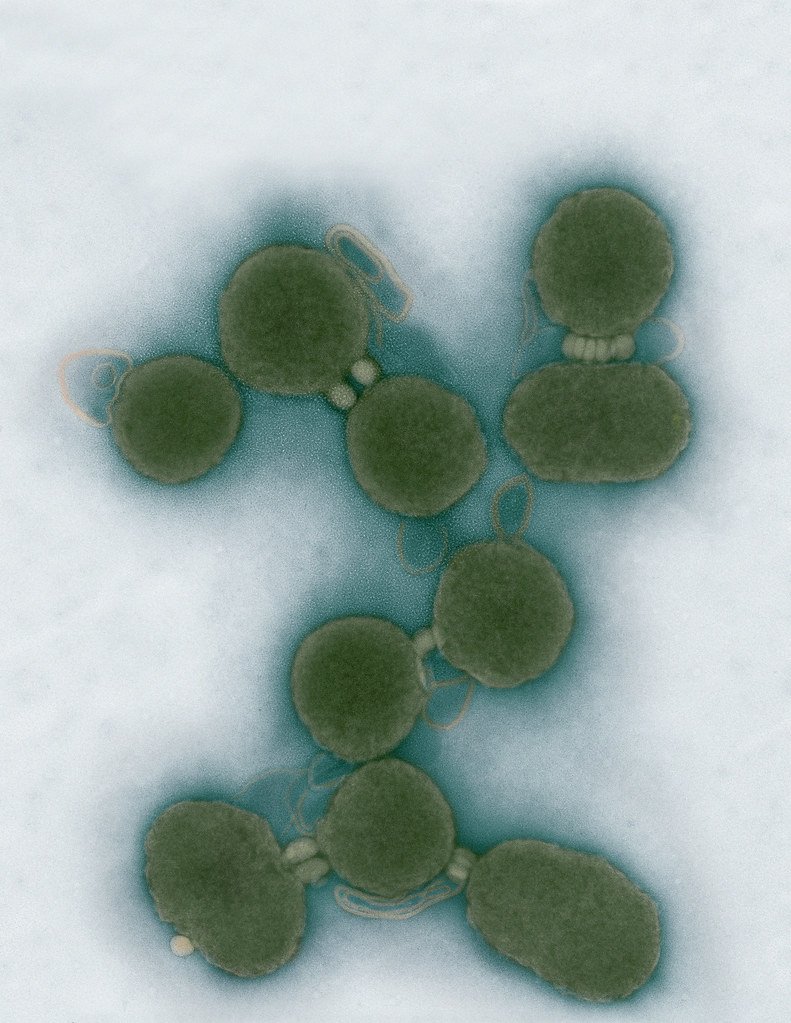
Aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Cells using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Freshly fixed cells were stained using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Scanning Electron Micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1
Scanning electron micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1. Samples were post-fixed in osmium tetroxide, dehydrated and critical point dried with CO2 , then visualized using a Hitachi SU6600 scanning electron microscope at 2.0 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

The Assembly of a Synthetic M. mycoides Genome in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

M. mycoides JCVI-syn 1.0 and WT M. mycoides
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Creating Bacteria from Prokaryotic Genomes Engineered in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
See more on the first self-replicating synthetic bacterial cell.
Minimal Cell

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.
Leadership

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D.
Credit: Brett Shipe / J. Craig Venter Institute

Sanjay Vashee, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

John Glass, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
Scientists in the Lab

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
JCVI La Jolla Lab (Exterior)
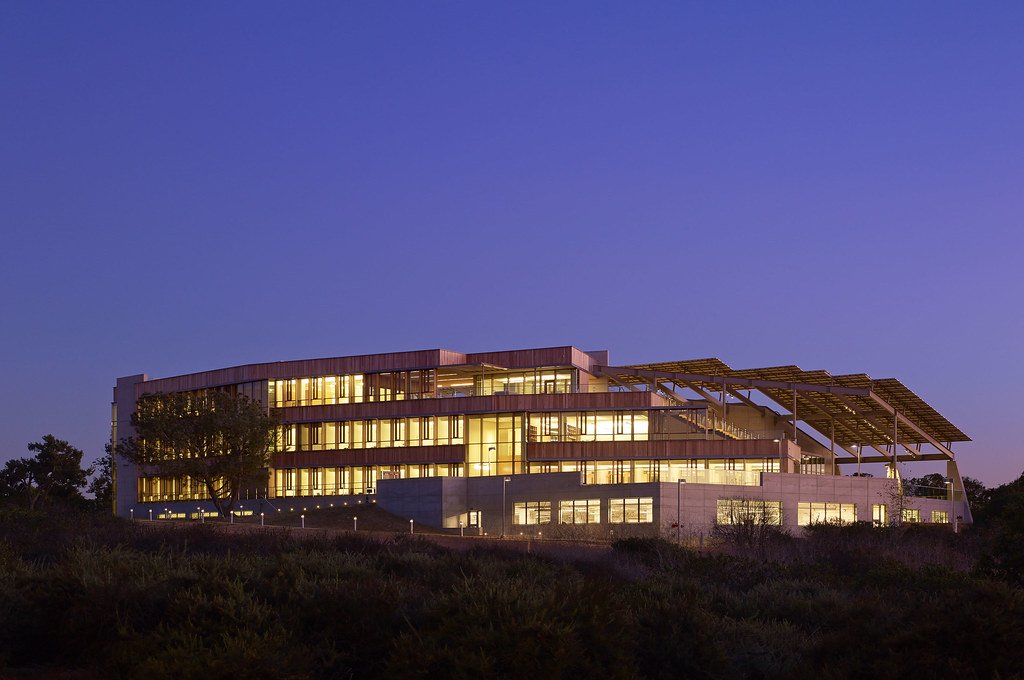

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
North facade at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
South facade from soccer field. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Northwest view. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Northeast view of main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East facing main entrance at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East facing main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Building main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
JCVI La Jolla north facade. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
JCVI La Jolla north facade detail. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
People at courtyard tables. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
2nd floor deck. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Looking west at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
First floor plaza looking south. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East main entrance closeup. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Stairs in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Detail of southwest corner. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Sunset off 3rd floor deck. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
From northwest at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Photovoltaics looking west towards ocean. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.
JCVI La Jolla Lab (Interior)

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Wet lab with people. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Single cell analyzer with researcher. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Mili-Q water purifier. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Lab bench work. Green plugs can be seen. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Cool room. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Confocal microscope. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Anaerobic glove box. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
JCVI staff at DNA sequencer. © Tim Griffith.