Media Center
Leading neuroscientist and AI geneticist Anders Dale, Ph.D. named president of J. Craig Venter Institute and joins Board
Through two multimillion-dollar NIH grants, Dr. Dale will continue leading key centers for the largest long-term studies of brain development and child health in the United States
Researchers design tools to develop vaccines more efficiently for African swine fever virus (ASFV)
The reverse-genetics system developed for ASFV may be adapted for other viruses, including lumpy skin disease, Zika, chikungunya, and Ebola viruses
Statement on cuts to National Institutes of Health funding
Disruptions or reductions in funding may irreparably harm biomedical research efforts at J. Craig Venter Institute and in the broader research ecosystem
Revolutionizing plastic waste management through biological upcycling
Innovative research transforms plastic waste into valuable chemicals, paving the way for a circular economy and sustainable space travel
Researchers call for global discussion about possible risks from “mirror bacteria”
Advocacy in Action: Effective Techniques for Shaping Science Policy
J. Craig Venter Institute awarded 5-year, $5M grant to lead Center for Innovative Recycling and Circular Economy (CIRCLE)
CIRCLE is one of the six new NSF Global Centers focused on advancing bioeconomy research to solve global challenges
Scientists discover molecular predictors of toxic algal blooms that pose health risk, ecological and economic harm
Genes in the algae Pseudo-nitzschia genus have been identified that act as a warning beacon for a dangerous neurotoxin
Prebys Introduces 2024 Grant Funding to Enhance Career Opportunities for Youth Across San Diego County
Organizations Receiving Part of the $5.89 Million Foster a Thriving San Diego Workforce
Prebys funds 24 grantees as part of a commitment to ensuring San Diego County youth are thriving and actively engaged in their communities
Passing of former J. Craig Venter Institute Trustee Bill Walton
Pages
Media Contact
Related
England, Here We Come!
In calm and clear conditions on May 11 Sorcerer II set sail for Plymouth, England. We enjoyed our brief stay in the Azores, but we were all excited to get to the U.K. and complete our North Atlantic crossing. As I mentioned in previous entries, we took samples near areas studied by...
Land Horta! The Sorcerer II on Faial Island, the Azores
We sailed into Horta on the island of Failal Saturday, May 9th around 1pm. The Sorcerer II crew was excited to visit the island but then again, we were just happy to walk on land and sleep in a bed that was not rolling from side to side! As usual when we arrive in a new port, we cleared...
North Atlantic Transit
After four days in Bermuda reconnecting with colleagues at BIOS and preparing for sampling across the North Atlantic, Sorcerer II departed on April 29th enroute to the port of Horta located on the island of Faial in the Azores. There are nine islands in the Azores archipelago which is...
Bermuda: Back to Where We Started
Sorcerer II arrived in Bermuda around 7 p.m. on Saturday April 25th after a five day, 1,000 mile sail from Fort Lauderdale, Florida. During the crossing, the crew experienced some challenging weather to say the least. Two samples were collected, and the CTD data confirmed what the J....
The Search for Environmental “Gems” Continues
As an original crew member of the Sorcerer II circumnavigation that began in 2003, I had not been sailing/sampling on the boat since September 2007. I arrived in Florida with a mixture of emotions. Although life on board can be tedious, I was excited to return and embark on this next leg of...
Back on Land
We arrive in Ft. Lauderdale and are all glad to be back on land for a few days. But we were also elated by the success of the first part of the expedition. This first journey was difficult because we had to deploy and test new equipment, to sample a diverse array of environments and...
Through the Canal
We are now out in the warm and saline Caribbean Sea, and the waters are an intense blue. The waters are so blue, there is very little in them: we drop the CTD and barely get 0.25 micrograms of Chlorophyll per liter all the way to the 50 meter mark. The clear waters of the Caribbean are very...
Miraflores Locks
We passed through the gigantic Miraflores locks on the Pacific side of the Panama Canal this morning, and now we are in front of the Smithsonian Tropical Research Station on Lake Gatun. The Sorcerer has sampled here on two other occasions, so to continue our time course evaluation, we ready the...
Going Green to Blue
As we round the southern most point on our trip we notice that the water has gone from blue to green, and that there appear to be surface current and eddies in the water. We decide to stop and have a look with the CTD. As we lower the instrument from the aft cockpit, we encounter a layer of...
Costa Rican Dome
In Nicaraguan waters is a regular spring upwelling event sometimes referred to as the Costa Rican dome. Winds blow across the Central American Isthmus near Lake Nicaragua and contribute to an upwelling of nutrient rich waters. These nutrients enable phytoplankton to grow, and as we approach the...
Pages
Public Health is the Next Big Thing at UC San Diego
Researchers have swapped the genome of gut germ E. coli for an artificial one
By creating a new genome, scientists could create organisms tailored to produce desirable compounds
Genetically modified bacteria-killing viruses used on patient for first time
Hair claimed to belong to Leonardo da Vinci to undergo DNA testing
Critics, however, argue that this effort is flawed from the beginning
Students learn about genomics, a life in science, at J. Craig Venter Institute
Pages
Logos
The JCVI logo is presented in two formats: stacked and inline. Both are acceptable, with no preference towards either. Any use of the J. Craig Venter Institute logo or name must be cleared through the JCVI Marketing and Communications team. Please submit requests to info@jcvi.org.
To download, choose a version below, right-click, and select “save link as” or similar.
Images
Following are images of our facilities, research areas, and staff for use in news media, education, and noncommercial applications, given attribution noted with each image. If you require something that is not provided or would like to use the image in a commercial application please reach out to the JCVI Marketing and Communications team at info@jcvi.org.
Human Genome

The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter
gff2ps achieved another genome landmark to visualize the annotation of the first published human diploid genome, included as Poster S1 of “The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter” (Levy et al., PLoS Biology, 5(10):e254, 2007). Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).

Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly
We have drawn the map of the Human Genome with gff2ps. 22 autosomic, X and Y chromosomes were displayed in a big poster appearing as Figure 1 of “The Sequence of the Human Genome” (Venter et al., Science, 291(5507):1304-1351, 2001). The single chromosome pictures can be accessed from here to visualize the web version of the “Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly” poster. Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).
Synthetic Cell

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D. and Hamilton O. Smith, M.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Hamilton O. Smith, M.D. and Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D.
Credit: Brett Shipe / J. Craig Venter Institute

Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

John Glass, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Dan Gibson, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Carole Lartigue, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Synthetic Biology Team
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
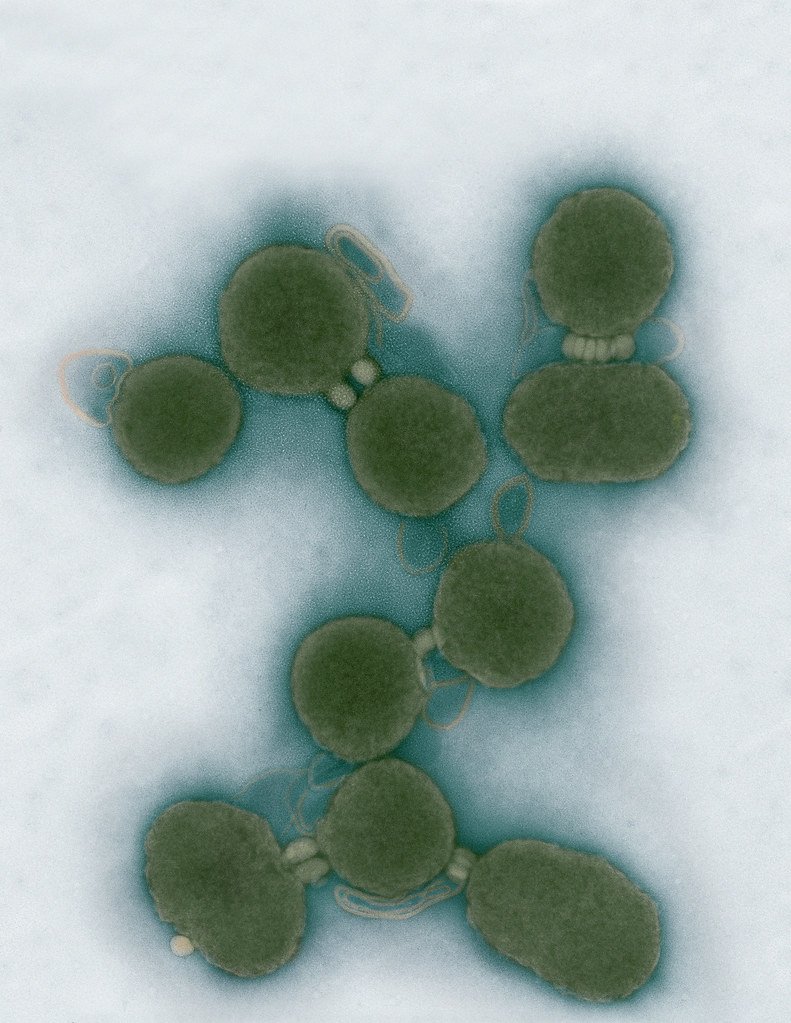
Aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Cells using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Freshly fixed cells were stained using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Scanning Electron Micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1
Scanning electron micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1. Samples were post-fixed in osmium tetroxide, dehydrated and critical point dried with CO2 , then visualized using a Hitachi SU6600 scanning electron microscope at 2.0 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

The Assembly of a Synthetic M. mycoides Genome in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

M. mycoides JCVI-syn 1.0 and WT M. mycoides
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Creating Bacteria from Prokaryotic Genomes Engineered in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
See more on the first self-replicating synthetic bacterial cell.
Minimal Cell

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.
Leadership

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D.
Credit: Brett Shipe / J. Craig Venter Institute

Sanjay Vashee, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

John Glass, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
Scientists in the Lab

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
JCVI La Jolla Lab (Exterior)
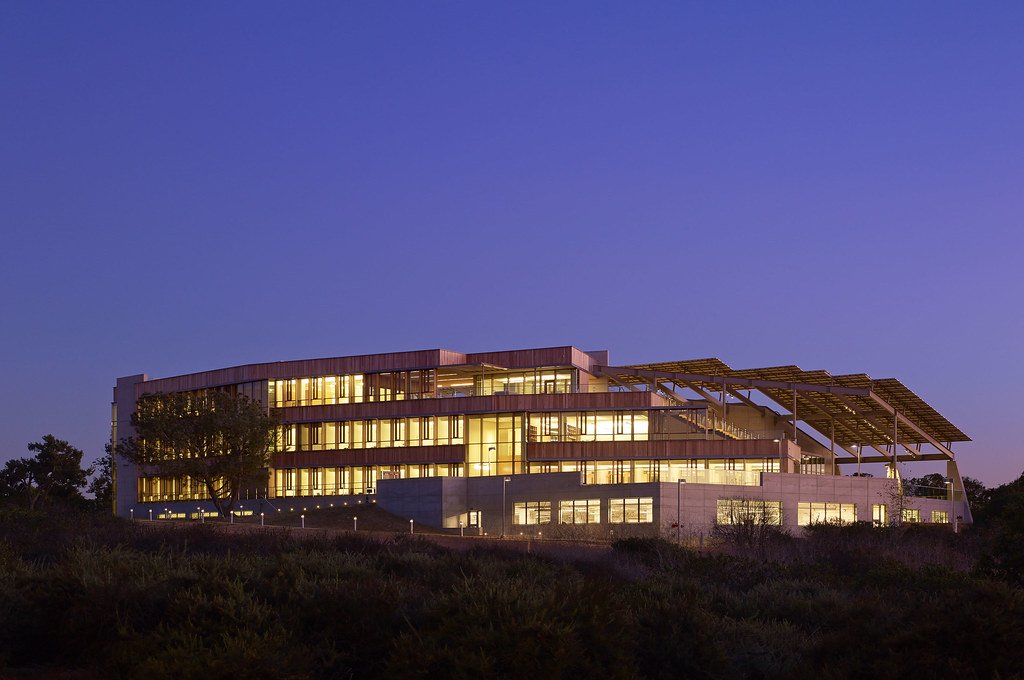

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
North facade at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
South facade from soccer field. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Northwest view. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Northeast view of main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East facing main entrance at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East facing main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Building main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
JCVI La Jolla north facade. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
JCVI La Jolla north facade detail. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
People at courtyard tables. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
2nd floor deck. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Looking west at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
First floor plaza looking south. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East main entrance closeup. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Stairs in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Detail of southwest corner. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Sunset off 3rd floor deck. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
From northwest at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Photovoltaics looking west towards ocean. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.