Media Center
Emory School of Nursing faculty member receives research grant from The ALS Association
J. Craig Venter Institute is a major partner, providing whole genome sequencing and data analysis needed to identify microbial makeup of ALS patients
Al Gore to lead global ‘healthy planet, healthy lives’ forum in Switzerland
Former US Vice President to address climate solutions in Montreux
JCVI President Karen Nelson to speak on “getting to the guts of health and disease”
J. Craig Venter Institute and UC San Diego Develop Phage Treatment as Potential Cure for Alcoholic Liver Disease
Team targeted specific toxin-producing strains of the bacterium, Enterococcus faecalis, which is shown to be responsible for most liver damage
San Diego Unified STEAM Leadership Series and the Salk Institute for Biological Studies Present: “The Places Your Imagination Takes You”—The 5th Annual Women in Biotech at the Salk
New Study Explores Unique Ways Diatoms Metabolize Nitrogen, Enabling Them to Thrive in Dynamic Environments
New Bioinformatics Hub at UChicago Enables Next-Gen Infectious Disease Research
NIH-funded resource merges pathogen databases and adds AI capabilities
JCVI/AADR Fall Focused Symposium
Integrating Omic Datasets Towards Translation
Combining Antibiotics, Researchers Deliver One-Two Punch against Ubiquitous Bacterium
CWRU/Cleveland VA findings in mouse models could make inroads against superbugs
J. Craig Venter will deliver the Mendel Lecture June 18th at the European Human Genetics Conference.
Craig Venter is the founder, chairman and CEO of the J. Craig Venter Institute in La Jolla, CA, United States. He will be giving the Mendel Lecture on Tuesday June 18 at 13.30 hrs. He talked to Mary Rice about his life and work.
Zymo Research Recognized by NASA for its Support of Research Aboard the International Space Station
DNA/RNA Shield™ Protects Biological Samples Even in Space
Pages
Media Contact
Related
Honoring Native American Heritage Month: bridging gaps in research and representation
As we celebrate Native American Heritage Month this November, we take time to recognize the vast diversity, rich heritage, and cultural contributions of Native American communities throughout American history. It’s also crucial to reflect on the historical and ongoing challenges faced by...
Hispanic Heritage Month
Hispanic Heritage Month, celebrated annually from September 15 to October 15, is a dedicated time to honor and recognize the rich cultural contributions and diverse histories of Hispanic Americans. The observance begins on September 15, the anniversary of independence for several Latin American...
Bright minds, bold discoveries: celebrating Jewish American leaders in science
Established by presidential proclamation in 2006, the month of May is recognized as Jewish American Heritage Month (JAHM). The month-long observance is designed as a time to honor and celebrate the achievements and impact of Jewish individuals and communities throughout American history. JAHM...
Celebrating innovation: pioneering AANHPI scientists who changed the world
May marks Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and Pacific Islander (AANHPI) Heritage Month, a time to celebrate the rich contributions of these communities across all fields, particularly in science. The AANHPI community is incredibly diverse, encompassing many cultures and ethnicities....
Celebrating the spectrum: Notable autistic scientists who redefined discovery
April is World Autism Awareness Month, a time to celebrate the unique strengths and experiences of autistic individuals and raise awareness about the challenges they face in their daily lives. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects how a person...
In celebration and recognition of Arab American Heritage Month
Arab American Heritage Month serves as a platform to honor and celebrate the rich cultural heritage, experiences, and enduring contributions of Arab Americans to our society. It is a time to recognize the resilience, creativity, and achievements of Arab Americans across various fields, from art...
Highlighting Women in STEM
March is a month dedicated to celebrating the incredible achievements and contributions of women throughout history. This year, we’d like to turn the spotlight towards the remarkable women who have revolutionized the scientific landscape. Throughout history, women in science faced significant...
Black History Month 2024
February marks the annual observance of Black History Month, a time to recognize and honor the rich heritage, achievements, and ongoing struggles of Black people. Founded and championed by historian Carter G. Woodson to ensure Black voices and contributions were not erased from traditional...
Rally for Medical Research
While my day job is an outreach coordinator and bioinformatic analyst at JCVI, supporting the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC), I also have a longstanding interest in science advocacy. As a graduate student at Keck Graduate Institute, I was selected to be part of an...
PRIDE in STEM
Updated 2023-06-09 AT JCVI, we know first-hand that a career in science and technology can be a fulfilling and rewarding way for individuals to make a real impact on the world around us. The STEM fields are shaping our lives and are fueling social progress. The involvement of LGBTQ+...
Pages
After saving countless lives, Nobel laureate Hamilton Smith retires as his own health falters
He has been a fixture in San Diego science for decades
The 'Wondrous Map': Charting of the Human Genome, 20 Years Later
Twenty years ago, President Bill Clinton announced completion of what was arguably one of the greatest advances of the modern era: the first draft sequence of the human genome.
Craig Venter: 20 years of decoding the human genome
The human genome is 99% decoded, the American geneticist Craig Venter announced two decades ago. What has the deciphering brought us since then?
Scientists in La Jolla Make Progress Understanding New Coronavirus Strain
Gene Drives: New and Improved
As the science advances, policy-makers and regulators need to develop responses that reflect the latest developments and the diversity of approaches and applications.
Pink shoes and a lab jacket: Finding your way as a female scientist
Women in science tell high school girls they, too, can change the world
PEOPLE IN YOUR NEIGHBORHOOD: Jazz piano in La Jolla scientist Clyde Hutchison’s DNA
How AI can help us decode immunity
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will be the keys to unraveling how the human immune system prevents and controls disease
Construction of an Escherichia coli genome with fewer codons sets records
The biggest synthetic genome so far has been made, with a smaller set of amino-acid-encoding codons than usual — raising the prospect of encoding proteins that contain unnatural amino-acid residues.
Pages
Logos
The JCVI logo is presented in two formats: stacked and inline. Both are acceptable, with no preference towards either. Any use of the J. Craig Venter Institute logo or name must be cleared through the JCVI Marketing and Communications team. Please submit requests to info@jcvi.org.
To download, choose a version below, right-click, and select “save link as” or similar.
Images
Following are images of our facilities, research areas, and staff for use in news media, education, and noncommercial applications, given attribution noted with each image. If you require something that is not provided or would like to use the image in a commercial application please reach out to the JCVI Marketing and Communications team at info@jcvi.org.
Human Genome

The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter
gff2ps achieved another genome landmark to visualize the annotation of the first published human diploid genome, included as Poster S1 of “The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter” (Levy et al., PLoS Biology, 5(10):e254, 2007). Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).

Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly
We have drawn the map of the Human Genome with gff2ps. 22 autosomic, X and Y chromosomes were displayed in a big poster appearing as Figure 1 of “The Sequence of the Human Genome” (Venter et al., Science, 291(5507):1304-1351, 2001). The single chromosome pictures can be accessed from here to visualize the web version of the “Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly” poster. Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).
Synthetic Cell

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D. and Hamilton O. Smith, M.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Hamilton O. Smith, M.D. and Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D.
Credit: Brett Shipe / J. Craig Venter Institute

Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

John Glass, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Dan Gibson, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Carole Lartigue, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Synthetic Biology Team
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
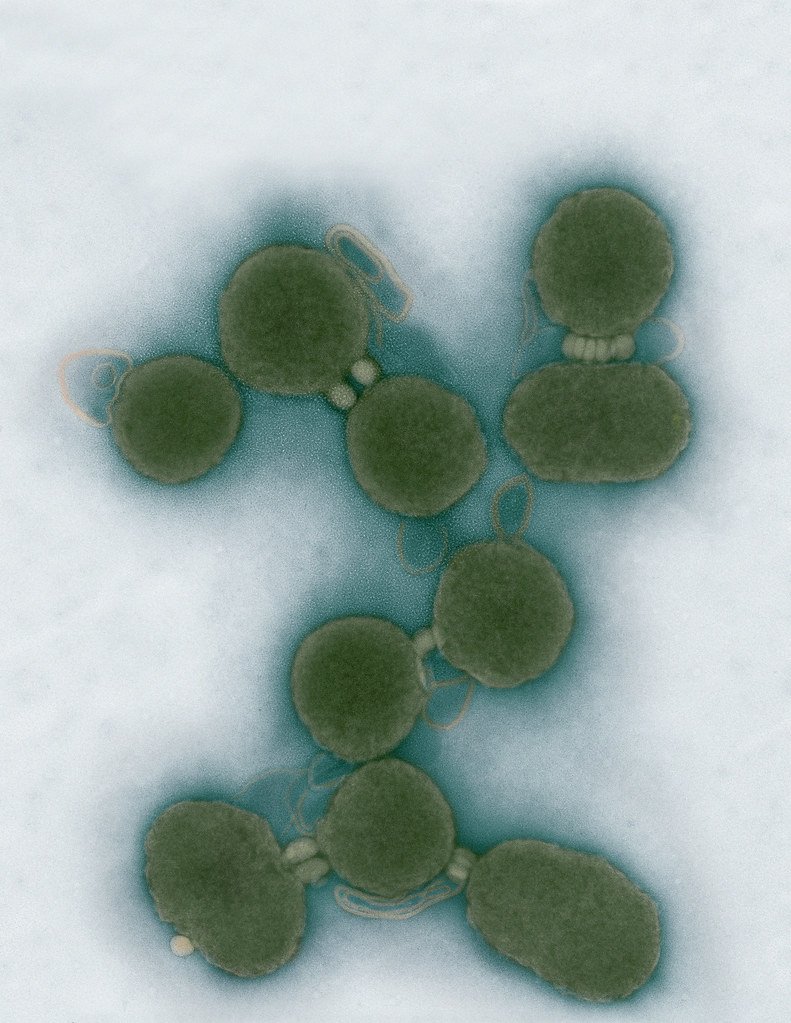
Aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Cells using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Freshly fixed cells were stained using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Scanning Electron Micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1
Scanning electron micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1. Samples were post-fixed in osmium tetroxide, dehydrated and critical point dried with CO2 , then visualized using a Hitachi SU6600 scanning electron microscope at 2.0 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

The Assembly of a Synthetic M. mycoides Genome in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

M. mycoides JCVI-syn 1.0 and WT M. mycoides
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Creating Bacteria from Prokaryotic Genomes Engineered in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
See more on the first self-replicating synthetic bacterial cell.
Minimal Cell

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.