Media Center
Trypanosoma brucei Genome Project at TIGR
10th International Genome Sequencing and Analysis Conference Information
The TIGR Zebrafish Gene Index version 1.0 BETA released
Gene Name Search for Arabidopsis sequencing project and Human sequencing project now available
The TIGR Arabidopsis Gene Index version 1.6 released
Human Gene Index new release version 3.3
Summer Fellowship/Internship Information and Application now available (Deadline for 1999 is Mar. 29th)
TIGR Web Site adds a site map and searching capabilities
TIGR Director J. Craig Venter, in the Sorcerer, undertakes sailing across the Atlantic along the same path as Columbus' Second Voyage
TIGR's 6th complete genome in 2 1/2 years is published
Pages
Media Contact
Related
Polynya opens in the Ross Sea
A helicopter pilot recently sent us an image of the area we are planning to sample, and the stable sea ice we intended to use as a platform for drilling and sampling is now a giant stretch of open seawater! A large opening like this is a polynya, a term borrowed from the Russian...
Christchurch, New Zealand
Greetings from Christchurch, New Zealand, the anteroom to Antarctica. My colleagues and I have been here for several days now, running last minute errands, getting equipped with cold weather gear, and waiting for a flight south to McMurdo Station. The flight here was remarkable only in it's...
Why Antarctica, and why now?
So why are you going to Antarctica, and why are you going now? A very logical question... basically we are traveling to Antarctica to study microscopic marine plants known as phytoplankton. These organisms range in size from bacteria to diatoms to colonial algae, but all phytoplankton have two...
Trip preparations (inaugural posting!)
Well, we have less than a week left, and we are finalizing and shipping the chemicals and equipment we will need for sampling below the sea ice in the Ross Sea. We have already shipped out several hundred pounds of gear, and more await us in storage down at McMurdo Station in Antarctica....
Going west!
After saying good bye to our new friends in Rostock/Warnemünde I was looking forward to coming back to Swedish waters, this time a bit saltier, on the west coast. There are two marine field stations on the Swedish west coast belonging to The Sven Lovén Center for Marine Sciences. Our first...
In the bloom...almost
Cyanobacterial blooms during the summer are reoccurring phenomena in the Baltic Sea. This summer we have already encountered the two main species responsible the blooms, Aphanizomenon sp. and the toxin producing Nodularia spumigena (see previous posts), but so far not in the abundance that...
In the Deep
After the brief stop in my hometown we continue our journey southward in the Baltic proper. Our first sampling site was the Landsort deep, the very deepest part of the Baltic Sea (459 meters!) and a long-term monitoring and sampling site for various Swedish and international scientists...
The Midnight Sun and Fermented Fish
We returned from Abisko on Thursday July 9th around 10 p.m. The next morning was very busy for the crew as we had to put the science gear back together, prepare the boat, and do local newspaper and radio interviews. Read the interview: paper Like the transect north, our...
ROAD TRIP! Watch Out Arctic Circle...the Sorcerer II Sampling Team is Coming Your Way!
After we arrived in Luleå, Jeremy, Karolina and I started packing for our road sampling trip to Lake Torneträsk, a freshwater lake located in the Arctic Circle. Dr. Erling Norrby had contacted Dr. Christer Jonasson, the deputy director of the Abisko Scientific Research Station, to help...
Sunset at Norrbyskär
It was another beautiful morning in the Gulf of Bothnia as we left Härnösand. We stopped at another sampling site before meeting with a boat from Umeå Marine Research Station (UMF). We were greeted by UMF scientist Dr. Johan Wikner and a television crew. We docked at Norrbyskär, a...
Pages
Leonardo Da Vinci: New family tree spans 21 generations, 690 years, finds 14 living male descendants
The surprising results of a decade-long investigation by Alessandro Vezzosi and Agnese Sabato provide a strong basis for advancing a project researching Leonardo da Vinci's DNA.
Genome Research Papers on Meningococcal Recombination, Psoriasis Variants in China, More
Sailing the Seas in Search of Microbes
Projects aimed at collecting big data about the ocean’s tiniest life forms continue to expand our view of the seas.
What the Public Should Not Know
J. Craig Venter, PhD, argues scientists have “a moral obligation to communicate what they're doing to the public,” and that more studies deserve greater public criticism.
Scientists coax cells with the world’s smallest genomes to reproduce normally
The discovery could sharpen scientists’ understanding of which functions are crucial for normal cells and what the many mysterious genes in these organisms are doing
San Diego arts, health, science and youth groups to share $71M from Prebys Foundation
The J. Craig Venter Institute is the recipient of three awards totaling more than $1.5M to study SARS-CoV-2 and heart disease
Reflections on the 20th Anniversary of the First Publication of the Human Genome
A new wave of research is needed to make ample use of humanity’s “most wondrous map”
Scientists rush to determine if mutant strain of coronavirus will deepen pandemic
U.S. researchers have been slow to perform the genetic sequencing that will help clarify the situation
Pages
Logos
The JCVI logo is presented in two formats: stacked and inline. Both are acceptable, with no preference towards either. Any use of the J. Craig Venter Institute logo or name must be cleared through the JCVI Marketing and Communications team. Please submit requests to info@jcvi.org.
To download, choose a version below, right-click, and select “save link as” or similar.
Images
Following are images of our facilities, research areas, and staff for use in news media, education, and noncommercial applications, given attribution noted with each image. If you require something that is not provided or would like to use the image in a commercial application please reach out to the JCVI Marketing and Communications team at info@jcvi.org.
Human Genome

The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter
gff2ps achieved another genome landmark to visualize the annotation of the first published human diploid genome, included as Poster S1 of “The Diploid Genome Sequence of J. Craig Venter” (Levy et al., PLoS Biology, 5(10):e254, 2007). Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).

Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly
We have drawn the map of the Human Genome with gff2ps. 22 autosomic, X and Y chromosomes were displayed in a big poster appearing as Figure 1 of “The Sequence of the Human Genome” (Venter et al., Science, 291(5507):1304-1351, 2001). The single chromosome pictures can be accessed from here to visualize the web version of the “Annotation of the Celera Human Genome Assembly” poster. Courtesy J.F. Abril / Computational Genomics Lab, Universitat de Barcelona (compgen.bio.ub.edu/Genome_Posters).
Synthetic Cell

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D. and Hamilton O. Smith, M.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Hamilton O. Smith, M.D. and Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D.
Credit: Brett Shipe / J. Craig Venter Institute

Clyde A. Hutchison III, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

John Glass, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Dan Gibson, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Carole Lartigue, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Synthetic Biology Team
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
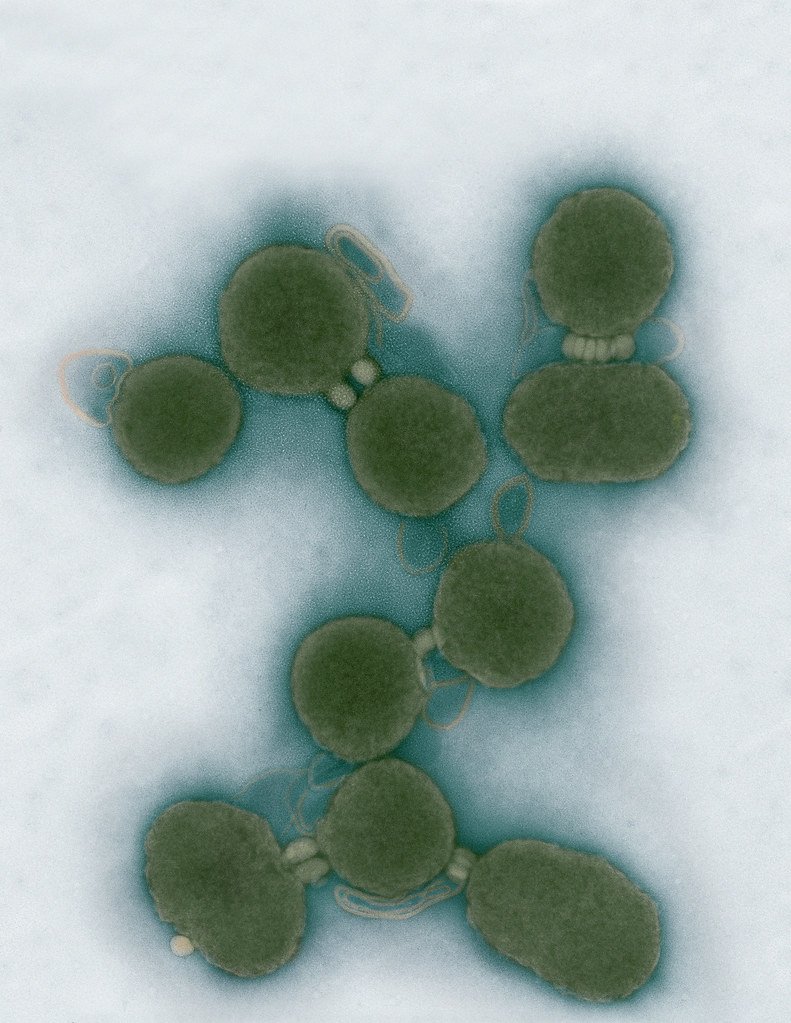
Aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of aggregated M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Cells using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Negatively stained transmission electron micrographs of dividing M. mycoides JCVI-syn1.0. Freshly fixed cells were stained using 1% uranyl acetate on pure carbon substrate visualized using JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope at 80 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Scanning Electron Micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1
Scanning electron micrographs of M. mycoides JCVI-syn1. Samples were post-fixed in osmium tetroxide, dehydrated and critical point dried with CO2 , then visualized using a Hitachi SU6600 scanning electron microscope at 2.0 keV. Electron micrographs were provided by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn1.0
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

The Assembly of a Synthetic M. mycoides Genome in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

M. mycoides JCVI-syn 1.0 and WT M. mycoides
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

Creating Bacteria from Prokaryotic Genomes Engineered in Yeast
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
See more on the first self-replicating synthetic bacterial cell.
Minimal Cell

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.

Minimal Cell — JCVI-syn3.0
Electron micrographs of clusters of JCVI-syn3.0 cells magnified about 15,000 times. This is the world’s first minimal bacterial cell. Its synthetic genome contains only 473 genes. Surprisingly, the functions of 149 of those genes are unknown. The images were made by Tom Deerinck and Mark Ellisman of the National Center for Imaging and Microscopy Research at the University of California at San Diego.
Leadership

J. Craig Venter, Ph.D.
Credit: Brett Shipe / J. Craig Venter Institute

Sanjay Vashee, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

John Glass, Ph.D.
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
Scientists in the Lab

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute

JCVI Scientists Working in Lab
Credit: J. Craig Venter Institute
JCVI La Jolla Lab (Exterior)
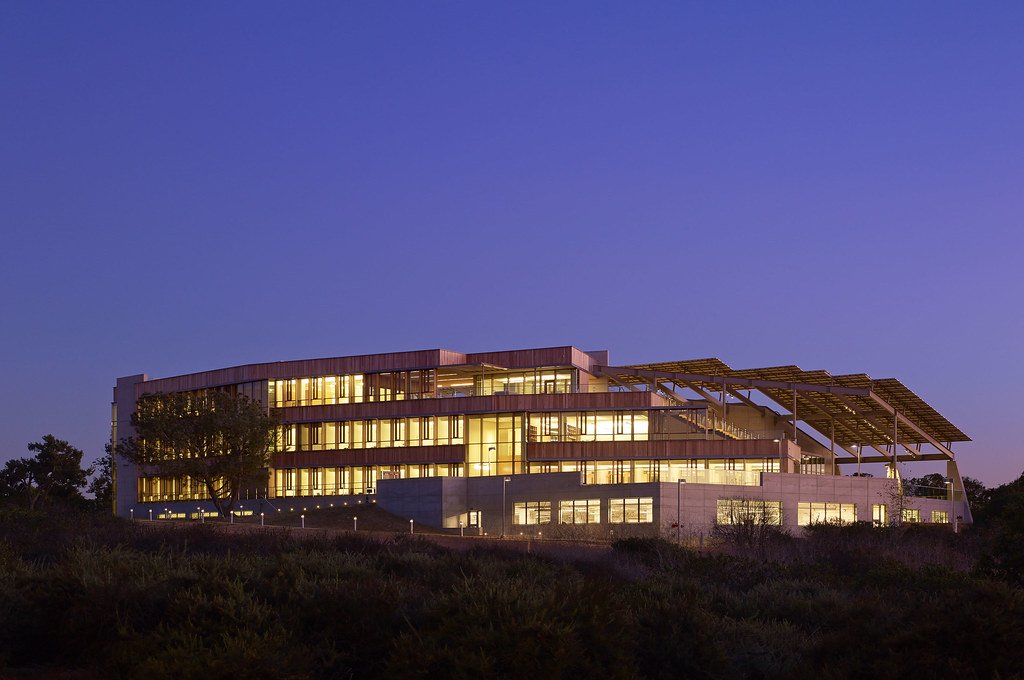

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
North facade at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
South facade from soccer field. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Northwest view. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Northeast view of main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East facing main entrance at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East facing main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Building main entrance. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
JCVI La Jolla north facade. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
JCVI La Jolla north facade detail. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Rock garden in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
People at courtyard tables. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
2nd floor deck. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Looking west at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
First floor plaza looking south. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
East main entrance closeup. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Stairs in courtyard. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Detail of southwest corner. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Sunset off 3rd floor deck. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
From northwest at dusk. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building exterior)
Photovoltaics looking west towards ocean. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.
JCVI La Jolla Lab (Interior)

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Wet lab with people. Nick Merrick © Hedrich Blessing Photographers.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Single cell analyzer with researcher. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Mili-Q water purifier. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Lab bench work. Green plugs can be seen. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Cool room. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Confocal microscope. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
Anaerobic glove box. © Tim Griffith.

J. Craig Venter Institute, La Jolla (building interior)
JCVI staff at DNA sequencer. © Tim Griffith.